Exosomes Identification Service
Online Inquiry- Service Details
- Case Study
Exosomes are involved in the pathological process of many diseases such as neurological diseases and cancer. At the same time, they also play an important function of mediating intercellular communication in normal physiological processes. Because they are rich in biomarkers, they can be used to monitor disease progression, treatment response, etc. Exosomes can also carry and deliver biomolecules and have the potential to become clinical drug delivery vehicles. In order to better study the function of exosomes, the first step is to identify exosomes.
The isolated exosomes need to be identified from three levels:
(1) Western blot (WB) to identify the surface markers of exosomes;
(2) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to identify the morphology of exosomes;
(3) Particle size analysis (NTA) to identify the size of exosomes.
The identification of exosomes includes the identification of protein components and nucleic acid components. Protein components: cytoskeleton proteins, signal transduction related proteins, metabolic enzymes, antigen binding and presentation related proteins. Nucleic acid components: Exosomes can also encapsulate mRNA, miRNA, lncRNA, mtDNA, circRNA, and transfer to other cells to play a biological role. The contents of Exosomes are also cell type specific.
Creative Proteomics has developed an exosome identification platform based on professional knowledge and advanced equipment to help accelerate the progress of your project.
Technology platform of exosomes identification service
To identify exosomes, WB must be used to identify whether the marker protein of exosomes is present in the sample. Exosomal membranes are rich in four transmembrane protein families (CD63, CD81 and CD9) involved in exosomal transport, heat shock protein families ((HSP60, HSP70, HSPA5, CCT2 and HSP90) and some cell-specific proteins Including A33 (derived from colonic epithelial cells), MHC-II (derived from antigen-presenting cells), CD86 (derived from antigen-presenting cells) and lactectin (immature dendritic cells). Among them, CD63, CD9, CD81 and TSG101 , HSP70, ALIX, etc. are the most commonly used extracellular vesicle markers.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) or transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and other electron microscopes have high resolution and can directly observe the morphology of exosomes in the sample and identify exosomes of different sizes.
Compared with other characterization methods, NTA technology has simpler sample processing, better guarantees the original state of exosomes, and faster detection speed.
- Flow cytometry: Detect biomarkers of exosomes.
Flow cytometry detection technology is relatively fast, suitable for high-throughput screening, and can analyze the size and volume of particles. Use antibodies corresponding to specific markers on the surface of exosomes for labeling, and then use flow cytometry to detect their positive expression to identify exosomes.
- Mass spectrometry: Qualitative and quantitative analysis of proteins.
Identification and quantitative analysis of proteins in exosomes by high-resolution mass spectrometry.
Case 1. Application of Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis for the Quantification of Exosomes in Human Urine [1]
Background
This study explores the use of Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) as a novel technique for identifying and quantifying nanoparticles, particularly exosomes, in human urine. Exosomes, small vesicles released by various cell types into biological fluids, including urine, carry valuable biomarkers that can shed light on kidney physiology and disease progression. Current methods for studying exosomes in urine are time-consuming and semi-quantitative, necessitating the development of more efficient approaches.
Samples
The study involved urine samples obtained from both healthy volunteers and individuals with specific conditions. For healthy volunteers, second-morning urine samples were collected from five participants. Additionally, urine samples were collected from a 16-year-old male with central diabetes insipidus (CDI) before and after routine desmopressin treatment. Samples were stored under various conditions for evaluation.
Technical Methods
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA): NTA is a technology used to size and count nanoparticles based on the Brownian motion of particles in solution. It involves directing laser light at a vesicle suspension and tracking the movement of individual nanoparticles over time. By analyzing their movement, the software calculates both the size and concentration of particles. Importantly, NTA was used to analyze urine samples without extensive sample processing.
Fluorescent Labeling of Exosomes: Antibodies against specific exosomal markers, such as CD24 and AQP2, were used to label exosomes in urine samples. This labeling allowed for the visualization and quantification of exosomes with reduced variability compared to unlabeled samples.
Exosome Isolation Methods: The study compared two common methods for isolating urinary exosomes: ultracentrifugation (UC) and ExoquickTM. Both methods aimed to concentrate exosomes but were found to also isolate non-exosomal particles.
Tracking Exosome Composition: NTA was applied to assess changes in exosome composition, particularly the upregulation of AQP2. This assessment was conducted in cell culture models, mouse urine samples, and a CDI patient's urine following desmopressin treatment. NTA demonstrated its ability to detect changes in exosome protein content rapidly.
Optimal Storage Conditions: The study evaluated the impact of different storage conditions on urinary nanoparticle preservation. Results indicated that freezing urine samples at -80°C with protease inhibitors was the most effective approach for retaining urinary nanoparticles. However, the study noted a significant loss of nanoparticles under all storage conditions, even within 2 hours of sample collection.
Results
- Successful identification and quantification of nanoparticles, including exosomes, in human urine using NTA.
- Confirmation of exosome-associated markers through fluorescent labeling with CD24 and AQP2 antibodies.
- Comparison of UC and ExoquickTM exosome isolation methods, highlighting the need for caution in assuming pure exosomal preparations.
- Rapid detection of changes in exosome protein content, notably AQP2 upregulation, using NTA in cell culture models, mouse urine, and a CDI patient's urine.
- Recommendation of optimal storage conditions for urinary nanoparticle preservation, with -80°C storage and protease inhibitors proving the most effective approach.
In summary, this study demonstrates the potential of NTA as a valuable tool for quantifying exosomes and other nanoparticles in human urine. It offers a rapid and efficient method for studying kidney physiology, disease, and biomarker discovery, while also emphasizing the importance of proper sample storage to preserve urinary nanoparticles effectively.
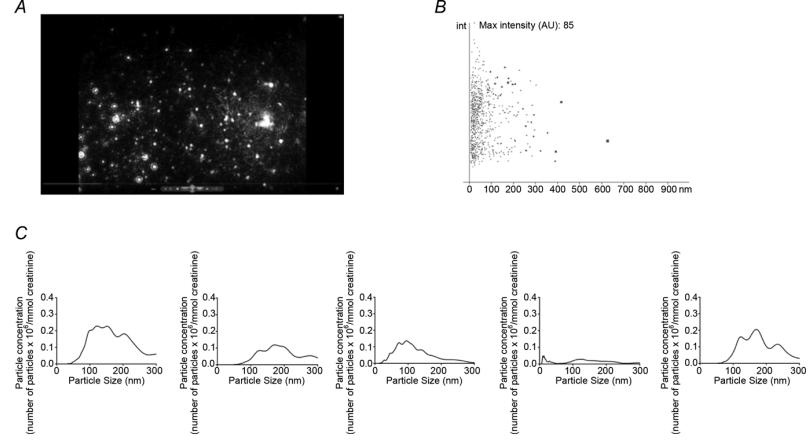 Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) of human urine samples
Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) of human urine samples
Case 2. Identification of Exosomes in Human Cerebrospinal Fluid: Implications for Neurological Disease Biomarker Discovery [2]
Background
Exosomes are small vesicles formed during the endosomal pathway and released into extracellular spaces. They are distinct in size, shape, and protein content and have been implicated in biomarker discovery and neurological diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. However, their presence in human cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) remained unconfirmed.
Sample
CSF was collected from 5 patients undergoing thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair. None of the patients had a history of neurological illness, and strict collection and preservation procedures were followed to maintain sample integrity.
Technical Methods
Exosome Concentration:
- After thawing, CSF underwent ultracentrifugation to pellet cellular debris.
- Supernatant was further ultracentrifuged to obtain the exosomal fraction.
- Protein content in the exosomal fraction was quantified using the BCA protein assay kit.
Western Blotting:
- The presence of exosomal markers, flotillin-1 and TSG101, was confirmed using Western blot analysis.
Sucrose Density Gradient:
- Isopycnic centrifugation on a sucrose step gradient was performed to confirm the localization of exosomal markers to specific density fractions, consistent with exosomes.
Electron Microscopy:
- Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was used to visualize exosome-like structures in the exosomal fraction. Anti-flotillin-1 antibody labeling confirmed the presence of exosomes.
Proteomic Analysis:
- Proteomic studies were conducted using FT-ICR mass spectrometry to profile the composition of the ultracentrifugation pellets from each study participant.
- Label-free quantification was employed to assess ion abundance across samples, revealing both shared and unique ions.
Results
Exosomes in CSF:
The study successfully demonstrated the presence of exosomes in human CSF through multiple lines of evidence, including enrichment of exosomal markers, visualization of exosome-like structures by TEM, and the presence of characteristic ions in mass spectrometry.
Variability:
- The study identified variability in exosomal composition across different individuals.
- Efforts to reduce contamination and improve exosome isolation techniques were recognized as important for future research.
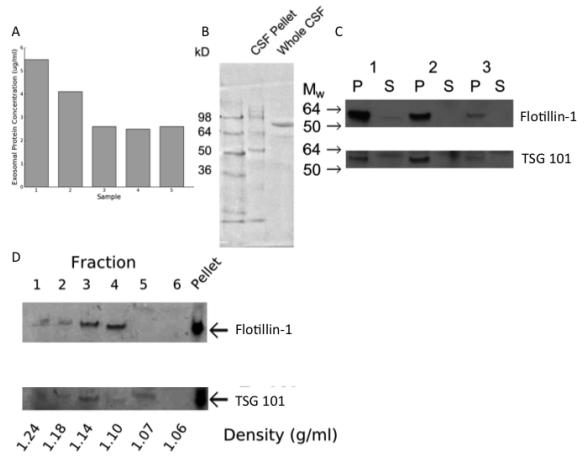 A) The pellet resulting from ultracentrifugation of human CSF contained protein.
A) The pellet resulting from ultracentrifugation of human CSF contained protein.
B) The size distribution of protein was different in the pellet resulting from ultracentrifugation of human CSF (CSF pellet) compared with uncentrifuged CSF (whole CSF).
C) Western blots for flotillin-1 and TSG-101 on the ultracentrifugation pellet (P) and supernatant (S) from CSF collected from 3 study participants (1-3).
D) Western blot for flotillin-1 and TSG101 on fractions obtained following isopycnic centrifugation.
References
- Oosthuyzen, Wilna, et al. "Quantification of human urinary exosomes by nanoparticle tracking analysis." The Journal of physiology 591.23 (2013): 5833-5842.
- Street, Jonathan M., et al. "Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human cerebrospinal fluid." Journal of translational medicine 10 (2012): 1-7.
Related Services
* For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.