Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) Service
Online InquiryCo-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) is a classical method for studying protein-protein interactions based on the specific interaction between antigen and antibody. Co-immunoprecipitation can be used to detect the interaction between two known proteins, or use known proteins to find unknown proteins that interact with them. Compared with other methods for detecting intermolecular interactions (GST pull down, etc.), the advantage of co-immunoprecipitation experiments is that the protein binding is completed in the cell, which can reflect the protein interaction in the natural state, and the results are more real and reliable.
Creative Proteomics has extensive proteomics experience and can provide co-immunoprecipitation (CO-IP) testing services for pharmaceutical companies or research institutions. This technology can verify whether two known proteins interact, and can also verify whether total proteins contain unknown proteins that interact with known proteins.
The Principle and Process of Co-IP Technology
When cells are lysed under non-denaturing conditions, many protein-protein interactions present in intact cells are preserved. For example, if a XY protein complex is present in the cell, X is immunoprecipitated with an X (bait protein) antibody. Then the protein Y (target protein) bound to X in the body will also be precipitated. Therefore, an antibody of X was added to the cell lysate to precipitate protein X, and then protein B was used to detect the presence of protein Y in the precipitate. If it exists, it indicates that there is an XY protein complex in the cell, and the protein XY interacts.
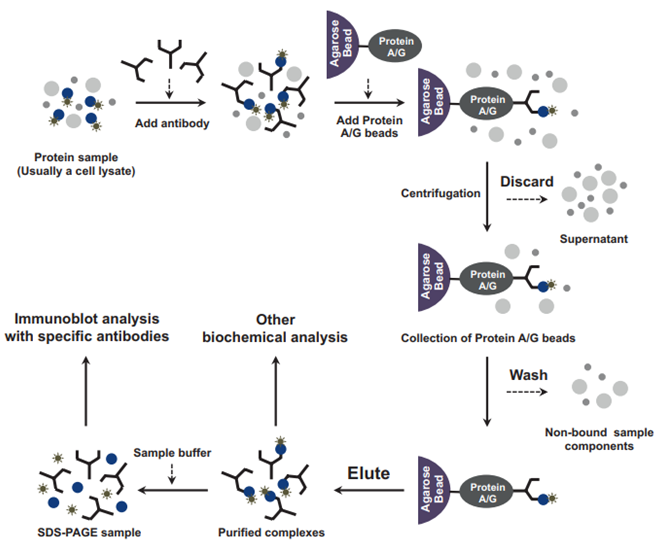
- Collect protein samples:
Endogenous interaction: Transfection of two proteins into the same cell by means of co-transfection of plasmids. After expression, the cells are collected and lysed to obtain protein samples.
Non-endogenous interactions: pretreatment of animal and plant tissues and organs containing target proteins. The cells are lysed to obtain a cell lysate. The bait protein (usually obtained by recombinant expression purification) is then added to the cell lysate to obtain a protein sample.
- Precipitation bait protein:
Magnetic bead-conjugated antibodies are used to precipitate bait proteins. If there is no specific antibody to the bait protein, you can tag the bait protein (Myc, HA, Flag, etc.), and then use the labeled antibody to precipitate the protein.
- SDS-PAGE, WB and MS detection
Advantages of Co-IP Protein Interaction Service:
- Interaction protein complexes can be isolated in their natural state
- Can detect in vitro and intracellular interactions
- Available in silver dyeing technology. 100 times more sensitive than Coomassie Brilliant Blue
- Equipped with high-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry supporting detection equipment, which can further analyze the detection results
- Repeat the experiment with quality control to exclude random factors to make the results more reliable
- With protein, antibody and other preparation platforms, you only need to provide the sequence to complete all experiments
Applications of Co-IP Technology
- Determine if two target proteins bind in vivo
- Identify new role profiles for a specific protein
- Isolate and obtain interacting protein complexes in their natural state
Sample Requirements
1. Provide protein samples: animal and plant tissues / organs or lysates containing bait protein and target protein;
2. Provide expression plasmid: The plasmid needs to be verified by sequencing, and the sequencing peak map is provided to prevent the base template of the gene template or the expression plasmid itself from mutating, which will cause experimental delays;
3. Provide the gene sequence: The customer provides the sequence, and Creative Proteomics is responsible for the expression of the bait protein or the target protein.
Want to Know about Other Subcellular Protein-protein Interaction Analysis Techniques?
References
- Lin J S, Lai E M. Protein–Protein Interactions: Co-Immunoprecipitation//Bacterial Protein Secretion Systems. Humana Press, New York, NY, 2017: 211-219.
- Romero-Fernandez W, Garcia-Barcelo M, Perez-Betancourt Y. Co-immunoprecipitation of Membrane-Bound Receptors from Subsynaptic Compartments//Co-Immunoprecipitation Methods for Brain Tissue. Humana Press, New York, NY, 2019: 137-145.
* For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.